
|
DoodleAssist: Progressive Interactive Line Art Generation with Latent Distribution Alignment
Haoran Mo,
Yulin Shen,
Edgar Simo-Serra and
Zeyu Wang
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics (TVCG 2025)
(CCF-A)
Project Page
Paper
Supplementary
Code
Abstract
Bibtex
Creating high-quality line art in a fast and controlled manner plays a crucial role in anime production and concept design. We present DoodleAssist, an interactive and progressive line art generation system controlled by sketches and prompts, which helps both experts and novices concretize their design intentions or explore possibilities. Built upon a controllable diffusion model, our system performs progressive generation based on the last generated line art, synthesizing regions corresponding to drawn or modified strokes while keeping the remaining ones unchanged. To facilitate this process, we propose a latent distribution alignment mechanism to enhance the transition between the two regions and allow seamless blending, thereby alleviating issues of region incoherence and line discontinuity. Finally, we also build a user interface that allows the convenient creation of line art through interactive sketching and prompts. Qualitative and quantitative comparisons against existing approaches and an in-depth user study demonstrate the effectiveness and usability of our system. Our system can benefit various applications such as anime concept design, drawing assistant, and creativity support for children.
@article{mo2025doodleassist,
title = {DoodleAssist: Progressive Interactive Line Art Generation with Latent Distribution Alignment},
author = {Mo, Haoran and Shen, Yulin and Simo-Serra, Edgar and Wang, Zeyu},
journal = {IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics (TVCG)},
year = {2025}
}
|

|
Joint Stroke Tracing and Correspondence for 2D Animation
Haoran Mo,
Chengying Gao* and
Ruomei Wang
ACM Transactions on Graphics (Presented at SIGGRAPH 2024)
(CCF-A)
Project Page
Paper
Supplementary
Code
Abstract
Bibtex
To alleviate human labor in redrawing keyframes with ordered vector strokes for automatic inbetweening,
we for the first time propose a joint stroke tracing and correspondence approach.
Given consecutive raster keyframes along with a single vector image of the starting frame as a guidance,
the approach generates vector drawings for the remaining keyframes while ensuring one-to-one stroke correspondence.
Our framework trained on clean line drawings generalizes to rough sketches
and the generated results can be imported into inbetweening systems to produce inbetween sequences.
Hence, the method is compatible with standard 2D animation workflow.
An adaptive spatial transformation module (ASTM) is introduced to handle non-rigid motions and stroke distortion.
We collect a dataset for training, with 10k+ pairs of raster frames and their vector drawings with stroke correspondence.
Comprehensive validations on real clean and rough animated frames manifest the effectiveness of our method and superiority to existing methods.
@article{mo2024joint,
title = {Joint Stroke Tracing and Correspondence for 2D Animation},
author = {Mo, Haoran and Gao, Chengying and Wang, Ruomei},
journal = {ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG)},
year = {2024}
}
|

|
General Virtual Sketching Framework for Vector Line Art
Haoran Mo,
Edgar Simo-Serra,
Chengying Gao*,
Changqing Zou and
Ruomei Wang
ACM Transactions on Graphics (SIGGRAPH 2021, Journal track)
(CCF-A)
Project Page
Paper
Supplementary
Code
Abstract
Bibtex
Vector line art plays an important role in graphic design, however, it is tedious to manually create.
We introduce a general framework to produce line drawings from a wide variety of images,
by learning a mapping from raster image space to vector image space.
Our approach is based on a recurrent neural network that draws the lines one by one.
A differentiable rasterization module allows for training with only supervised raster data.
We use a dynamic window around a virtual pen while drawing lines,
implemented with a proposed aligned cropping and differentiable pasting modules.
Furthermore, we develop a stroke regularization loss that encourages the model
to use fewer and longer strokes to simplify the resulting vector image.
Ablation studies and comparisons with existing methods corroborate the efficiency of our approach
which is able to generate visually better results in less computation time,
while generalizing better to a diversity of images and applications.
@article{mo2021virtualsketching,
title = {General Virtual Sketching Framework for Vector Line Art},
author = {Mo, Haoran and Simo-Serra, Edgar and Gao, Chengying and Zou, Changqing and Wang, Ruomei},
journal = {ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG)},
year = {2021},
volume = {40},
number = {4},
pages = {51:1--51:14}
}
|

|
Language-based Colorization of Scene Sketches
Changqing Zou#,
Haoran Mo#(equal contribution),
Chengying Gao*,
Ruofei Du and
Hongbo Fu
ACM Transactions on Graphics (SIGGRAPH Asia 2019, Journal track)
(CCF-A)
Project Page
Paper
Supplementary
Code
Slide
Abstract
Bibtex
Being natural, touchless, and fun-embracing, language-based inputs have been demonstrated effective
for various tasks from image generation to literacy education for children. This paper for the first
time presents a language-based system for interactive colorization of scene sketches, based on semantic
comprehension. The proposed system is built upon deep neural networks trained on a large-scale
repository of scene sketches and cartoon-style color images with text descriptions. Given a scene
sketch, our system allows users, via language-based instructions, to interactively localize and
colorize specific foreground object instances to meet various colorization requirements in a
progressive way. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach via comprehensive experimental
results including alternative studies, comparison with the state-of-the-art methods, and generalization
user studies. Given the unique characteristics of language-based inputs, we envision a combination of
our interface with a traditional scribble-based interface for a practical multimodal colorization
system, benefiting various applications.
@article{zouSA2019sketchcolorization,
title = {Language-based Colorization of Scene Sketches},
author = {Zou, Changqing and Mo, Haoran and Gao, Chengying and Du, Ruofei and Fu, Hongbo},
journal = {ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG)},
year = {2019},
volume = {38},
number = {6},
pages = {233:1--233:16}
}
|
|
DiFusion: Flexible Stylized Motion Generation Using Digest-and-Fusion Scheme
Yatian Wang,
Haoran Mo and
Chengying Gao*
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics (TVCG 2025)
(CCF-A)
Paper
Abstract
Bibtex
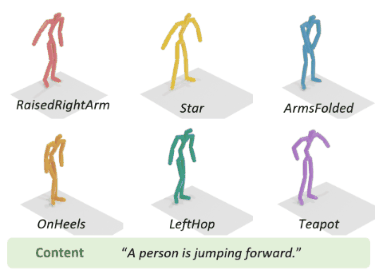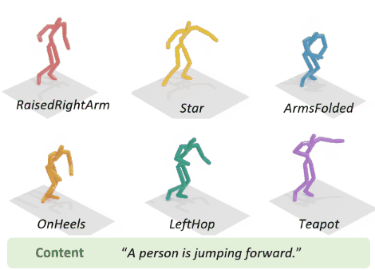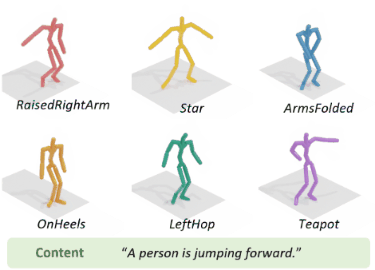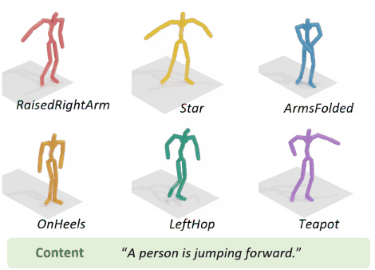
To address the issue of style expression in existing
text-driven human motion synthesis methods, we propose DiFusion, a framework for diversely stylized motion generation.
It offers flexible control of content through texts and style via
multiple modalities, i.e., textual labels or motion sequences. Our
approach employs a dual-condition motion latent diffusion model,
enabling independent control of content and style through flexible
input modalities. To tackle the issue of imbalanced complexity
between the text-motion and style-motion datasets, we propose
the Digest-and-Fusion training scheme, which digests domain
specific knowledge from both datasets and then adaptively fuses
them into a compatible manner. Comprehensive evaluations
demonstrate the effectiveness of our method and its superiority
over existing approaches in terms of content alignment, style
expressiveness, realism, and diversity. Additionally, our approach
can be extended to practical applications, such as motion style
interpolation.
@article{wang2025difusion,
title = {DiFusion: Flexible Stylized Motion Generation Using Digest-and-Fusion Scheme},
author = {Wang, Yatian and Mo, Haoran and Gao, Chengying},
journal = {IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics (TVCG)},
year = {2025}
}
|

|
SketchyScene: Richly-Annotated Scene Sketches
Changqing Zou#,
Qian Yu#,
Ruofei Du,
Haoran Mo,
Yi-Zhe Song,
Tao Xiang,
Chengying Gao,
Baoquan Chen* and
Hao Zhang
European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV 2018)
(CCF-B)
Project Page
Paper
Poster
Code
Abstract
Bibtex
We contribute the first large-scale dataset of scene
sketches, SketchyScene, with the goal of advancing research on sketch understanding at both the object
and scene level. The dataset is created through a novel and carefully designed crowdsourcing pipeline,
enabling users to efficiently generate large quantities realistic and diverse scene sketches.
SketchyScene contains more than 29,000 scene-level sketches, 7,000+ pairs of scene templates and photos,
and 11,000+ object sketches. All objects in the scene sketches have ground-truth semantic and instance
masks. The dataset is also highly scalable and extensible, easily allowing augmenting and/or changing
scene composition. We demonstrate the potential impact of SketchyScene by training new computational
models for semantic segmentation of scene sketches and showing how the new dataset enables several
applications including image retrieval, sketch colorization, editing, and captioning, etc.
@inproceedings{zou2018sketchyscene,
title={Sketchyscene: Richly-annotated scene sketches},
author={Zou, Changqing and Yu, Qian and Du, Ruofei and Mo, Haoran and Song, Yi-Zhe and Xiang, Tao and Gao, Chengying and Chen, Baoquan and Zhang, Hao},
booktitle={Proceedings of the european conference on computer vision (ECCV)},
pages={421--436},
year={2018}
}
|

















